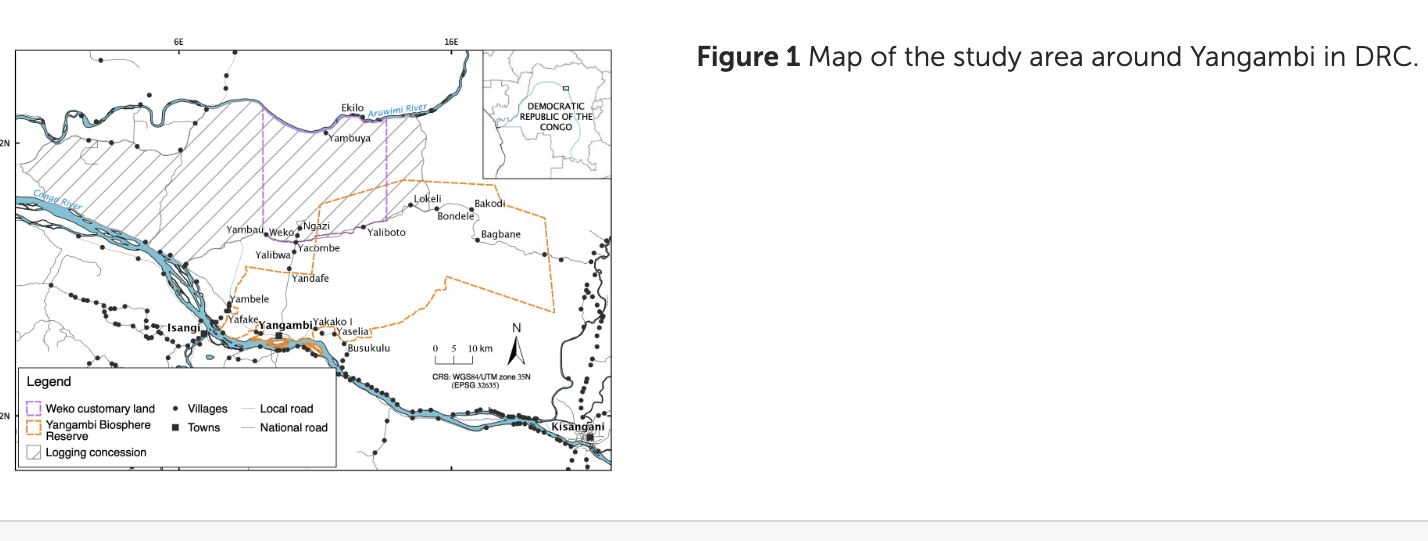
Since the second half of the 2000s, several options for implementing community-based forest management in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), like the local community forest concession (LCFC), have been discussed in the country’s technical and political circles. Proposals and pilot testing have increased in the last five years, but the funding of initiatives is often proposed for divergent purposes and taking different approaches. We reviewed current experiences in the Eastern province of the DRC and found that nobody has carried out an estimation of the financial returns of the business models they drew up for/with the communities involved. We therefore conducted a financial feasibility analysis for two case studies, estimating the costs of developing/implementing activities and the benefits expected for the communities within the next five years. Three main conclusions were drawn from the analysis: (1) most activities conducted under the LCFC model deal with rural development, and not with forestry operations per se; (2) several forestry activities such as biodiversity conservation or carbon sequestration are not detailed in the management documents and appear to have little legitimacy for local populations; (3) the two LCFCs show a negative financial performance because the inception and implementation costs are substantially higher than the medium-term profits. Community forestry is unlikely to develop in the DRC unless local people are guaranteed that it will contribute to improving their livelihoods, notably their financial and physical capital. This requires that LCFC initiatives focus on actual productive uses of forest resources, which financial performance is systematically assessed ex ante. A simplification of the legal constraints is also needed to reduce the cost of creating and managing a LCFC.